Many people write about language proficiency in the Skills section of their resume. As a result, the hours and money spent on language learning become invisible. Don’t make your HR manager look for a needle in a haystack: create a separate section for your language skills!
In this article you will learn:
- How to determine your level of language proficiency
- When knowledge of languages on a resume matters
- How to write about levels of language proficiency in a resume
- What the different levels of language proficiency are
- In which section of the resume you should add information about the levels of English
Foreign languages in summary. Language levels for a resume
Learning a foreign language tells the recruiter about the investment you’ve made in yourself. Most employers will be impressed that you know other languages. It doesn’t matter whether it’s Spanish, Chinese, French, Tagalog or Swahili. It takes time, effort and money to learn a new language.
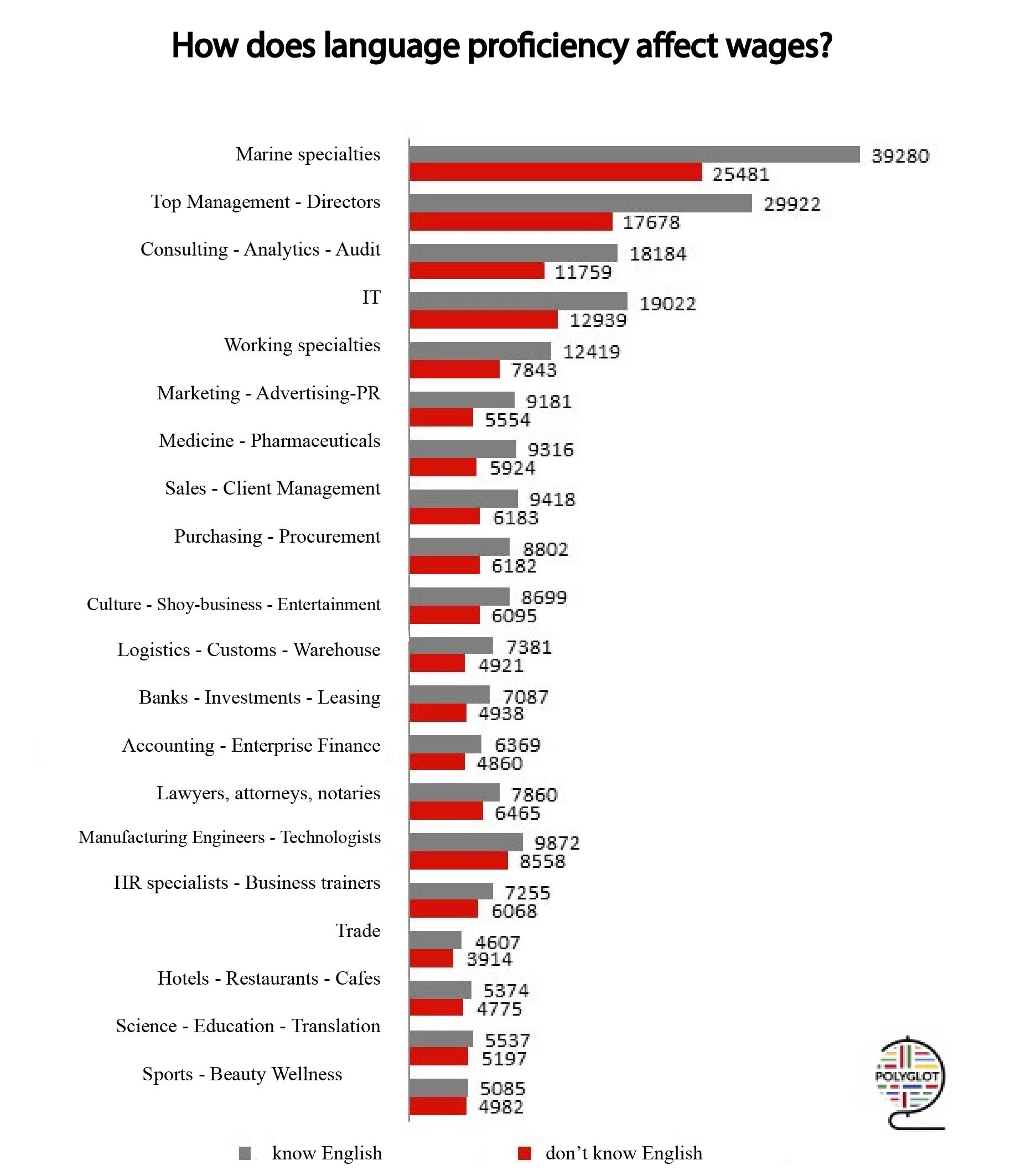
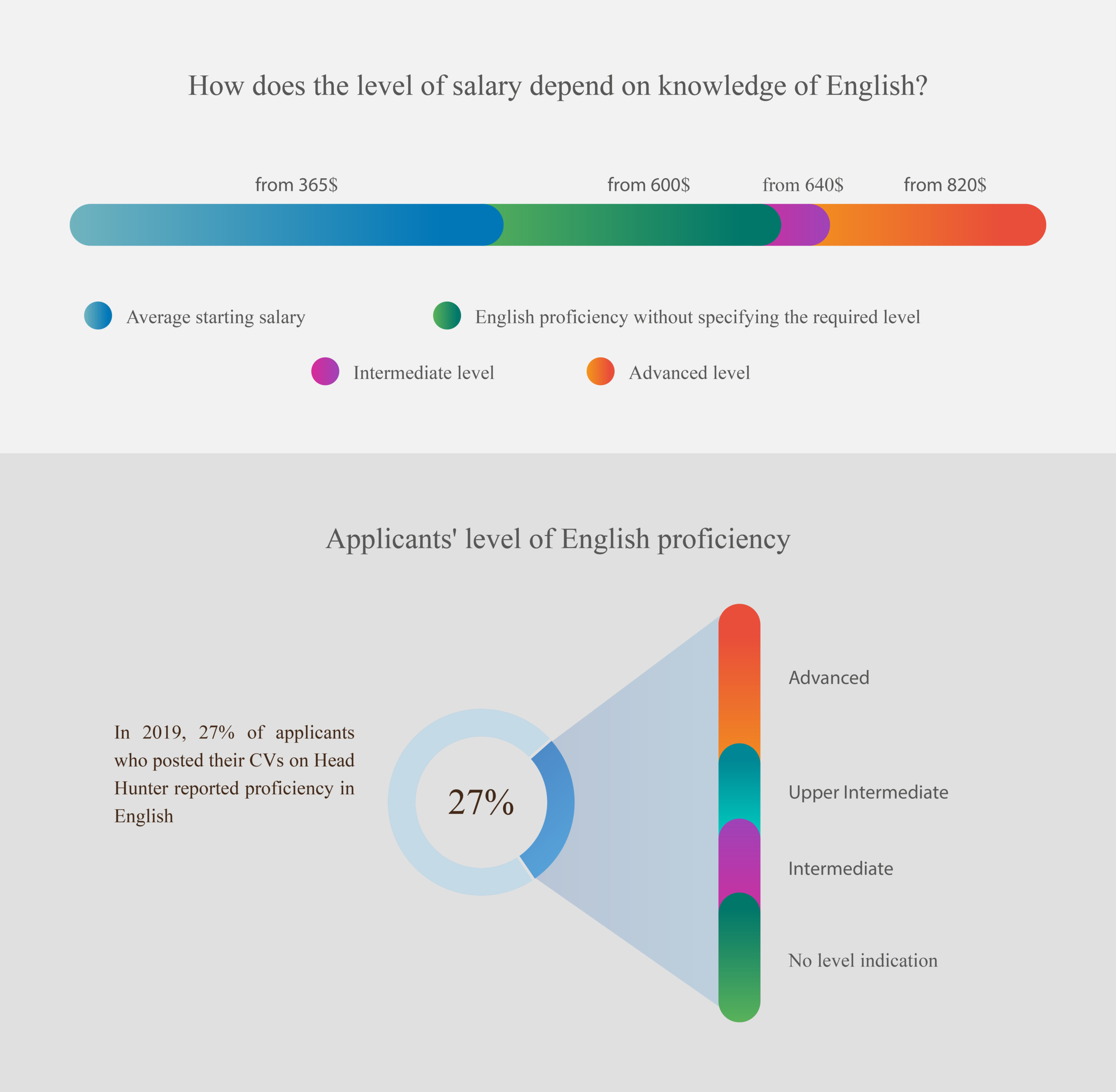
What are the most popular languages?
According to the portal gooverseas.com, people who know English, German, French or Spanish are the most sought-after by employers. However, those who speak Chinese, Japanese, Turkish, Hebrew, Dutch or Swedish earn more.
But before you list a language skill on your resume, you must first determine your level of proficiency in English, German, French, or other languages.
How to write about the level of language proficiency in the resume
- Create a separate section for your language skills
- Add it after the main sections of your resume (Purpose, Experience, Skills, and Education)
- Use a uniform description form
- Start with the language you speak best
An example of how to write about language skills in a resume:
American English – native
Brazilian Portuguese – fluent
Egyptian Arabic – spoken
Bravan Swahili – beginner
There are alternatives regarding the formulation of skill levels:
Advanced: native, fluent, above intermediate.
Intermediate level: intermediate, conversational, competent, professional.
Beginner: beginner, basic, below intermediate, limited.
Many applicants have a problem with language proficiency wording. For example, a candidate writes “Spoken English” and a recruiter thinks, “Can a candidate with a conversational level read and write the language, too?”
To avoid confusion, use the language proficiency scale.
Language proficiency in a resume
The most common types of qualifications are:
The Common European Framework for Languages (CEFR) is a foreign language proficiency level system used in the European Union. The base users of the language are rated as A1 or A2, independent users as B1 or B2, and experienced users as C1 or C2.

Basic (A1, A2)
A1
Someone on this level can introduce himself, ask a question and discuss personal information. For example, where s/he lives, the people s/he knows and the things s/he has. S/he can interact if the interlocutor speaks slowly, clearly and is ready to help.
A2
S/he can communicate in the context of tasks that require a direct exchange of information on familiar issues. S/he may be able to describe in simple terms aspects of his/her origin, immediate surroundings and questions in areas where necessary.
Middle level (B1, B2)
B1
Could create a simple text on topics that are familiar or of personal interest. Describes events and desires, briefly explains the reasons for changing opinions and plans.
B2
Can provide a clear, detailed answer on a wide range of issues and explain the point of view on the relevant issue, giving advantages and disadvantages of the various options.
Advanced level (C1)
Speaks fluently, without searching for expressions. Can use the language flexibly and effectively for social, academic and professional purposes.
Media Level (C2)
S/he distinguishes subtle shades of meaning even in difficult situations. Easily understands almost everything that s/he has heard or read.
Description of CEFR levels based on the article: How to write a resume in English?
ILR Interagency Language Roundtable Scale, United States – American classification of language proficiency levels. Developed for the US government, the ILR proficiency scale has 6 levels of language proficiency (0-5), plus an additional “+” for intermediate levels.
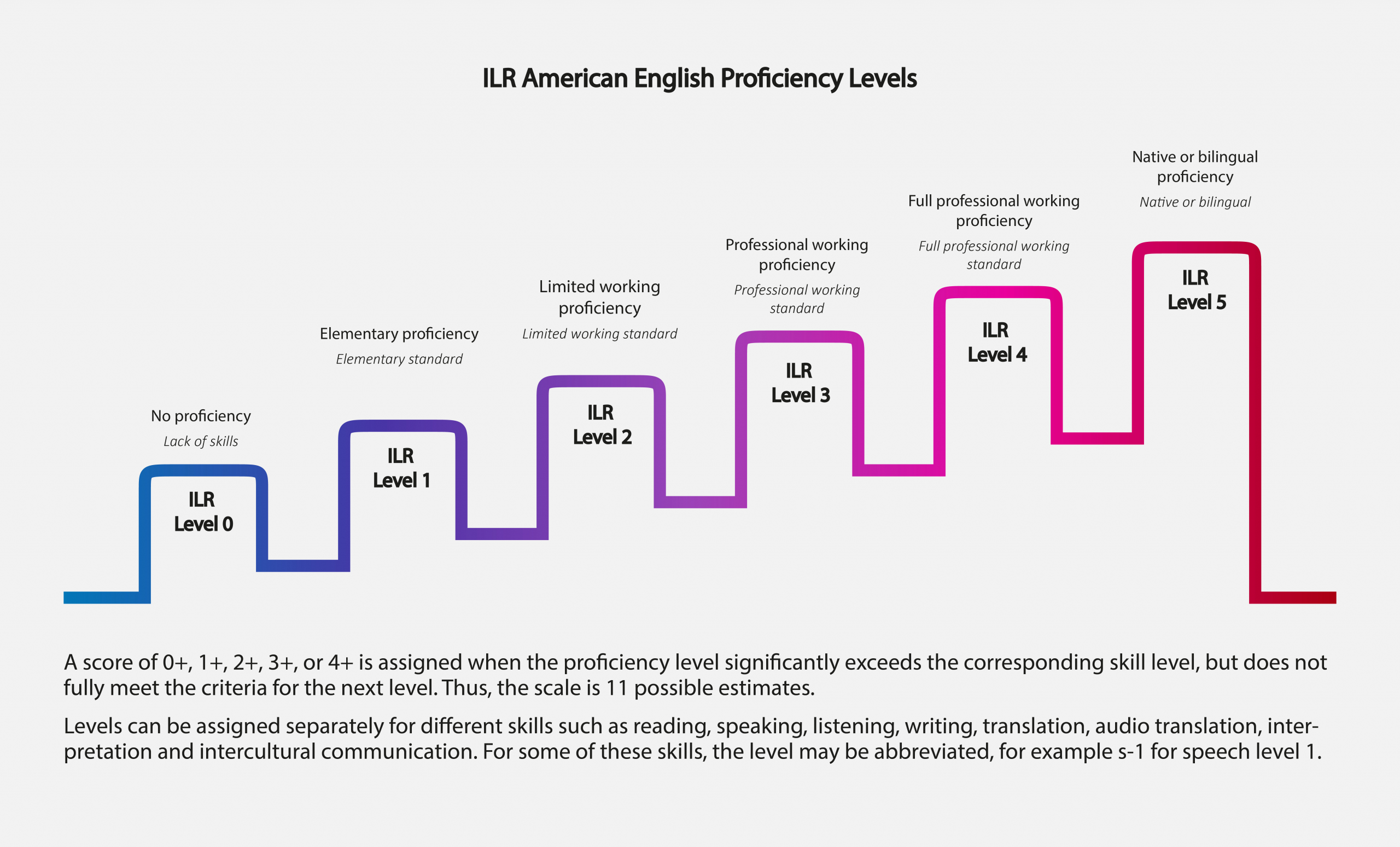
The American Council for the Teaching of Foreign Languages (ACTFL) is another widely used language proficiency scale. Language fluency levels include: Beginner (Low, Intermediate, High), Intermediate (Low, Intermediate, High), Advanced (Low, Intermediate, High), Superior and Excellent.
LinkedIn – The main business network uses its own level of language proficiency. In fact, they are a copy of the ILR language scale.
General terms used to describe levels of language proficiency
Basic – if you study a language, the basic knowledge will be identical to the knowledge of 101 or 102 other subjects. You know simple words and phrases, you have very limited reading skills and you can’t engage in conversations with native speakers. You are still having trouble with your choice of words and are constantly turning to the dictionary.
Conversational – You can have a conversation in a language, though not freely. The speed with which you are able to understand sentences remains slow, and your choice of words remains uncertain.
Experienced – the phrase «experienced language user» is often found in the resume. In linguistic terms, knowledge does not mean the same as mastery. To state that you are experienced in the language means that you are able to use the language orally and in writing, but not at the same level as a native speaker.
Fluency – Your level of proficiency means that you are fluent in this language and can read, write, talk and communicate in the same way as native speakers.
Examples for resume
When it comes to creating a language proficiency level summary section, the first step is to indicate the classification.
Here is an example of a summary section of language levels:
English – Level 5 (ILR)
Bengali – Level 4 (ILR)
North China – Level 3 (ILR)
In this example, we simply added the ILR level next to each language. In brackets, we added «ILR», so that the hiring manager knows what language scale we are using.
Here’s another example of a language summary section:
American English – Native / Bilingual (ILR Level 5)
Canadian French – Native / Bilingual (ILR Level 5)
Russian – full professional training (ILR level 4+)
Malay – Professional Skills (ILR Level 3)
Here we gave a level of language proficiency in LinkedIn. Although based on ILR, the section can still be interpreted, so we have added levels of language proficiency for the summary in parentheses.
To send resumes to European countries, use the CEFR scale:
British English – native / bilingual
Italian – certificate C1
Polish – level B2
Have you noticed the difference between Italian and Polish?
It means that the candidate has received an official certificate confirming his Italian at the C1 level, and he assessed his Polish as B2.
There is no single right way to add your language proficiency levels, but there are some mistakes that job seekers often make. How can you avoid them?
Be consistent. Do not mix the classification of language skills, even if you have the corresponding certificate (for example, one candidate reported having ILR 4+ in English and C1 in Hungarian).
Use the current rating system. For example, if you apply for employment in the EU, use the CEFR levels. Start with the language you know best, then go to the rest in descending order.
Your language skills are part of the skill set. To learn how to make the most of them, read this article.
How do I determine my level of language proficiency?
Often candidates either overestimate their abilities (which is almost like telling lies in the resume) or underestimate them (and do not sell themselves as they might).
Instead, select one of two options:
Independently evaluate your level or get a certificate. If this language is important for your work, for example, for editors and copywriters, you will receive an official assessment of your abilities by paying for the test.
In all other cases, self-assessment must work but only if you use official tests and documents.
The official ILR website offers several PDF files and guides to help you evaluate your own abilities. There are also self-assessment questionnaires for reading, speaking and listening.
In the CEFR scale, you can judge yourself by an official diagram that allows you to judge your skills in 5 areas: spoken interaction, spoken production, reading, conversation and writing.
In the ACTFL Proficiency Recommendation, evaluation is available on their website and updated once every few years. The 10-level scale is also divided into reading, writing, speaking and listening.
How to indicate language levels in the CV?
As soon as you assess your language proficiency, you should put it on your resume.
The first thing you have to do is figure out how important language proficiency is in a potential workplace. If it occupies one of the first places, you should create a separate section in your summary called «Languages». Companies that regularly do business with foreign organisations will surely put languages at the top of their qualification list.
If the requirement to know a language is secondary, it is enough to include it in the «Skills section» of your resume. The «Skills section» follows the work experience and the level of education. Read more about the correct structure and presentation of the resume here.
Conclusions
Most companies that require language skills prefer to employ native speakers. However, they can be quite expensive. A candidate who speaks a foreign language as an additional skill is a more viable alternative, especially when the level of proficiency is close or at the level of a native speaker.
The ability to speak foreign languages will always be considered a strength of the applicant, regardless of the specific requirements of the post. This is becoming increasingly important in the era of globalisation, as language skills provide the company with the inherent flexibility of business.
Try a smart template that solves the problem of interpreting your level of knowledge. CV2you constructor displays language skills graphically!